Xinchen Wang
王欣辰
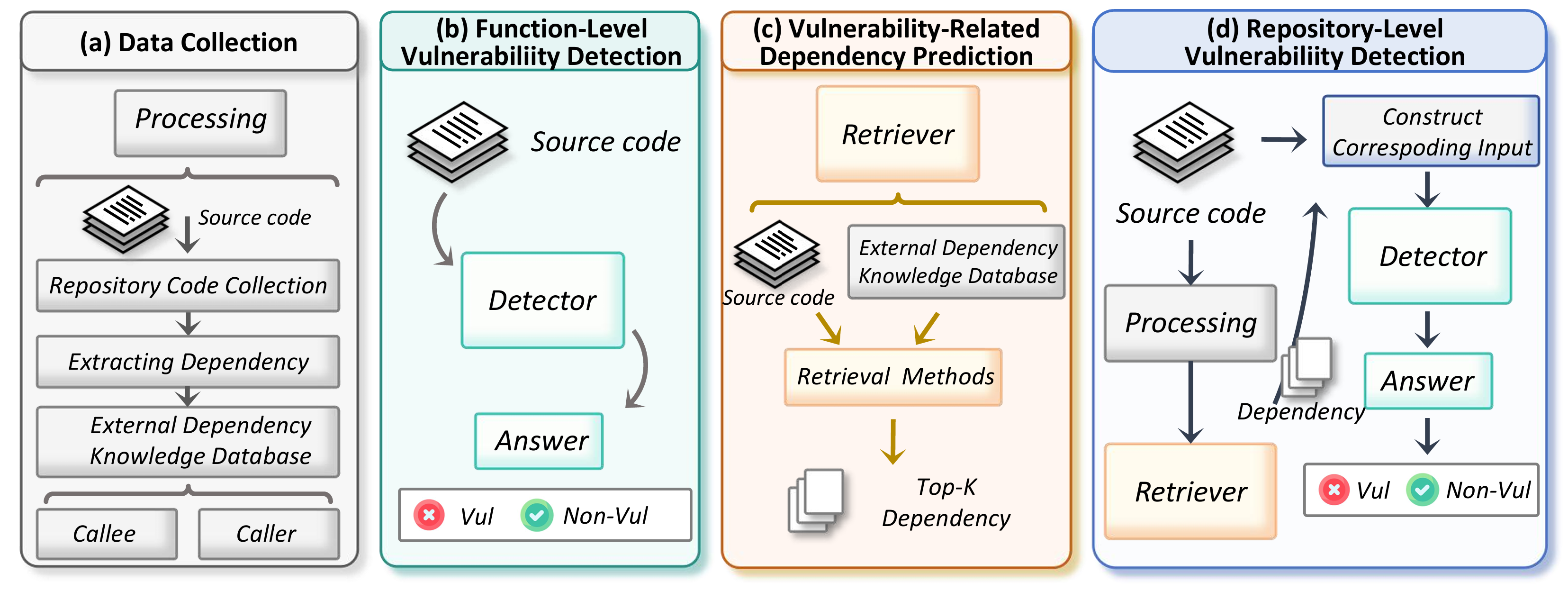
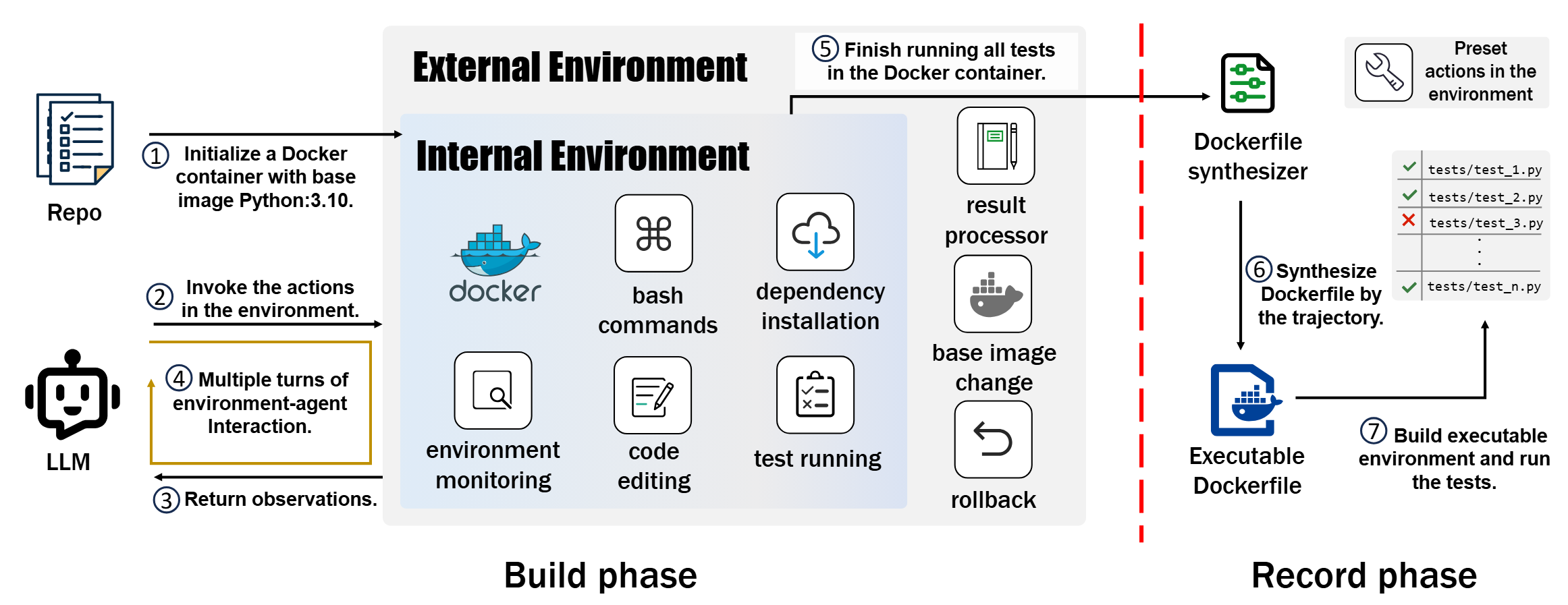
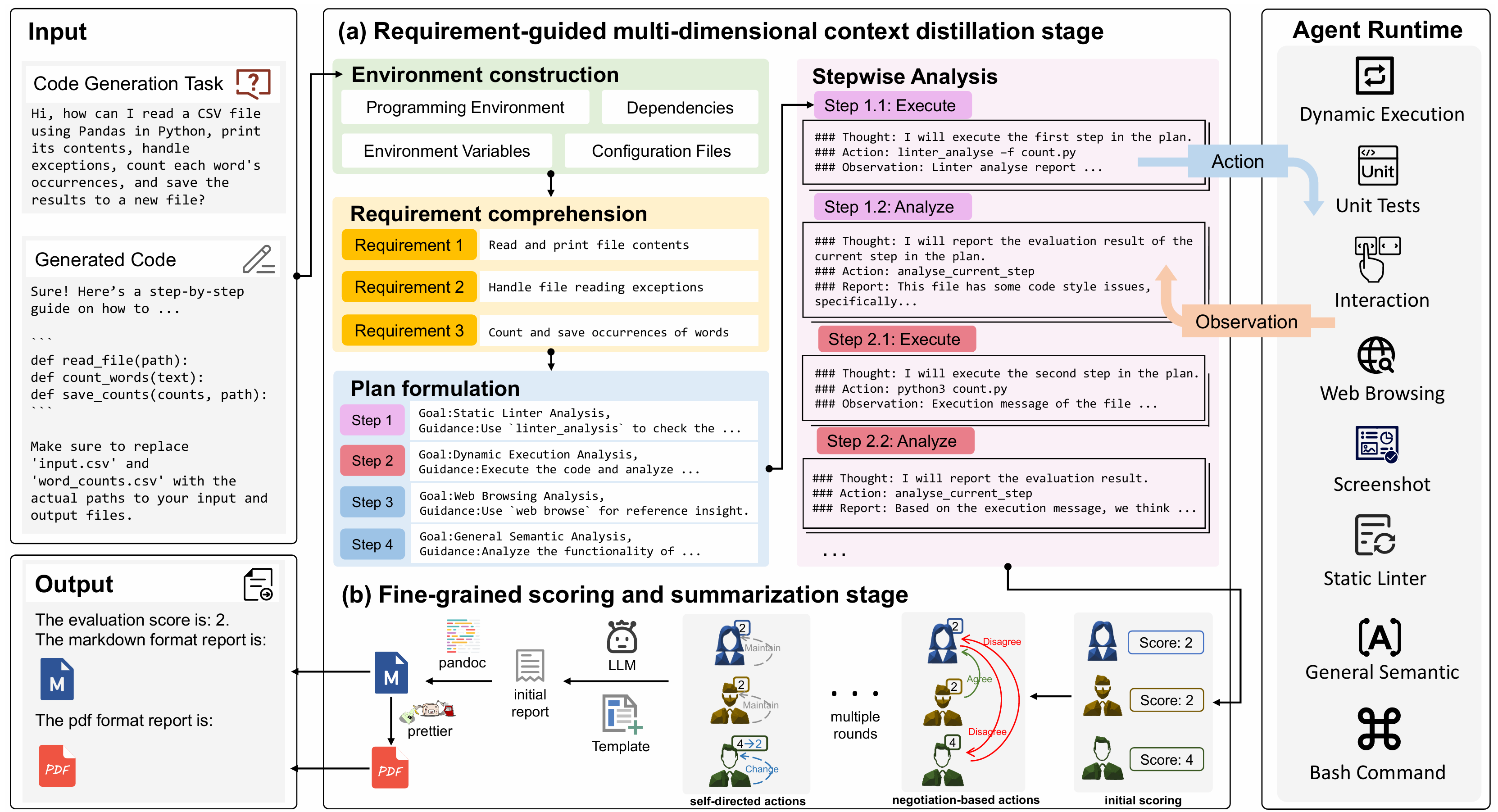
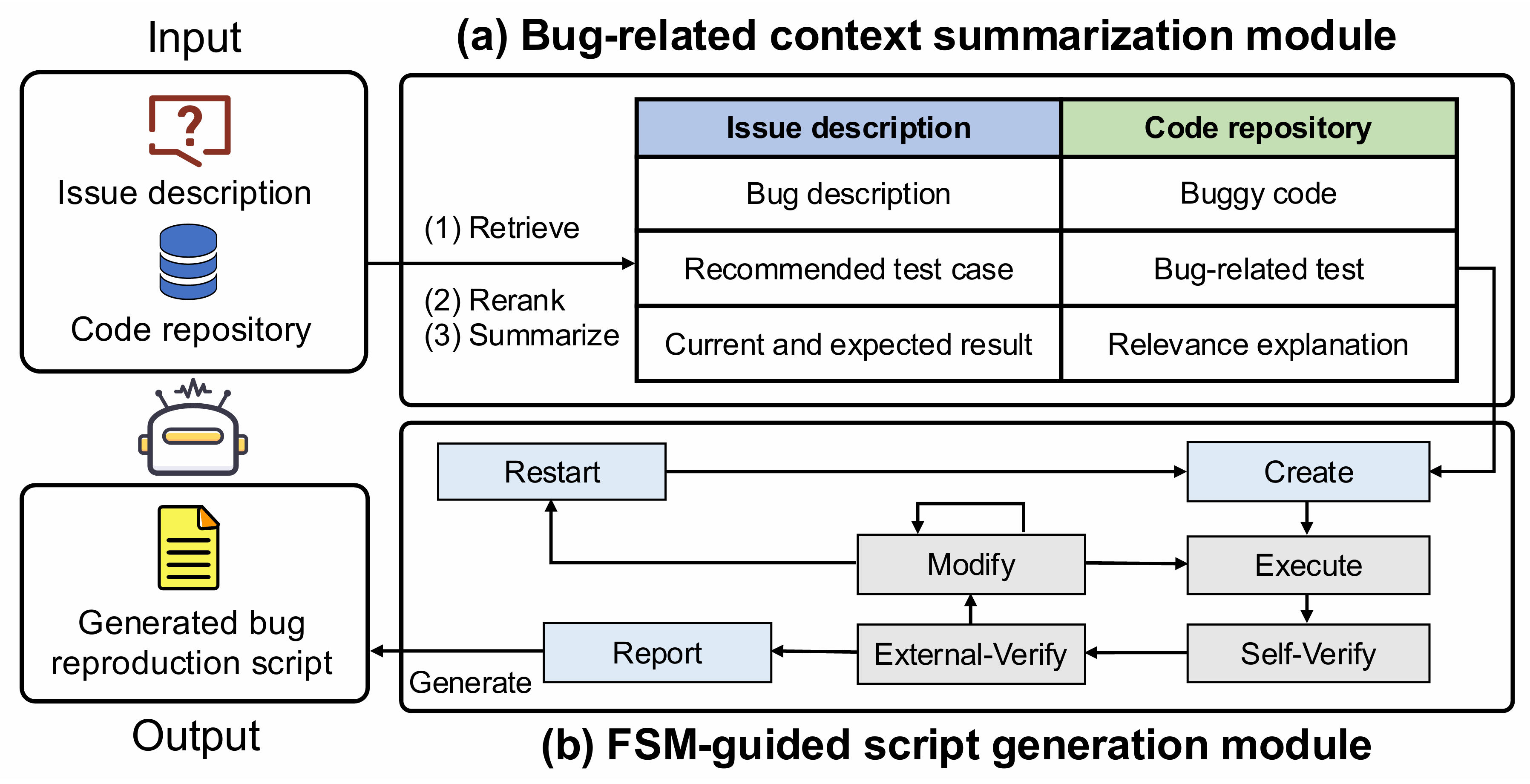
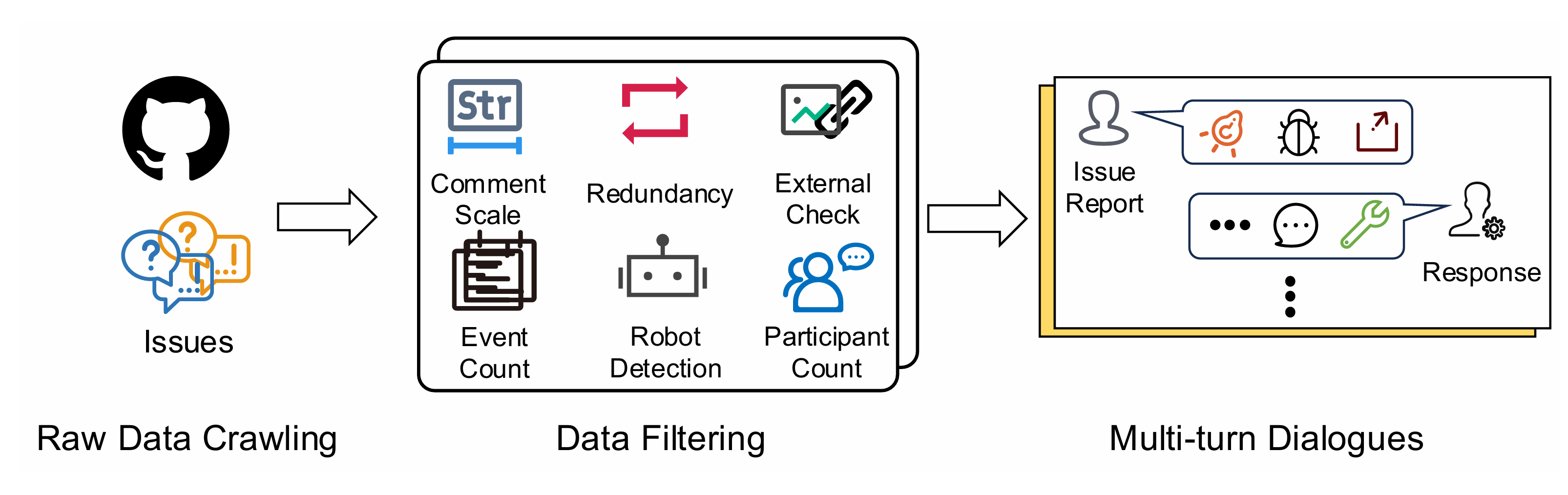
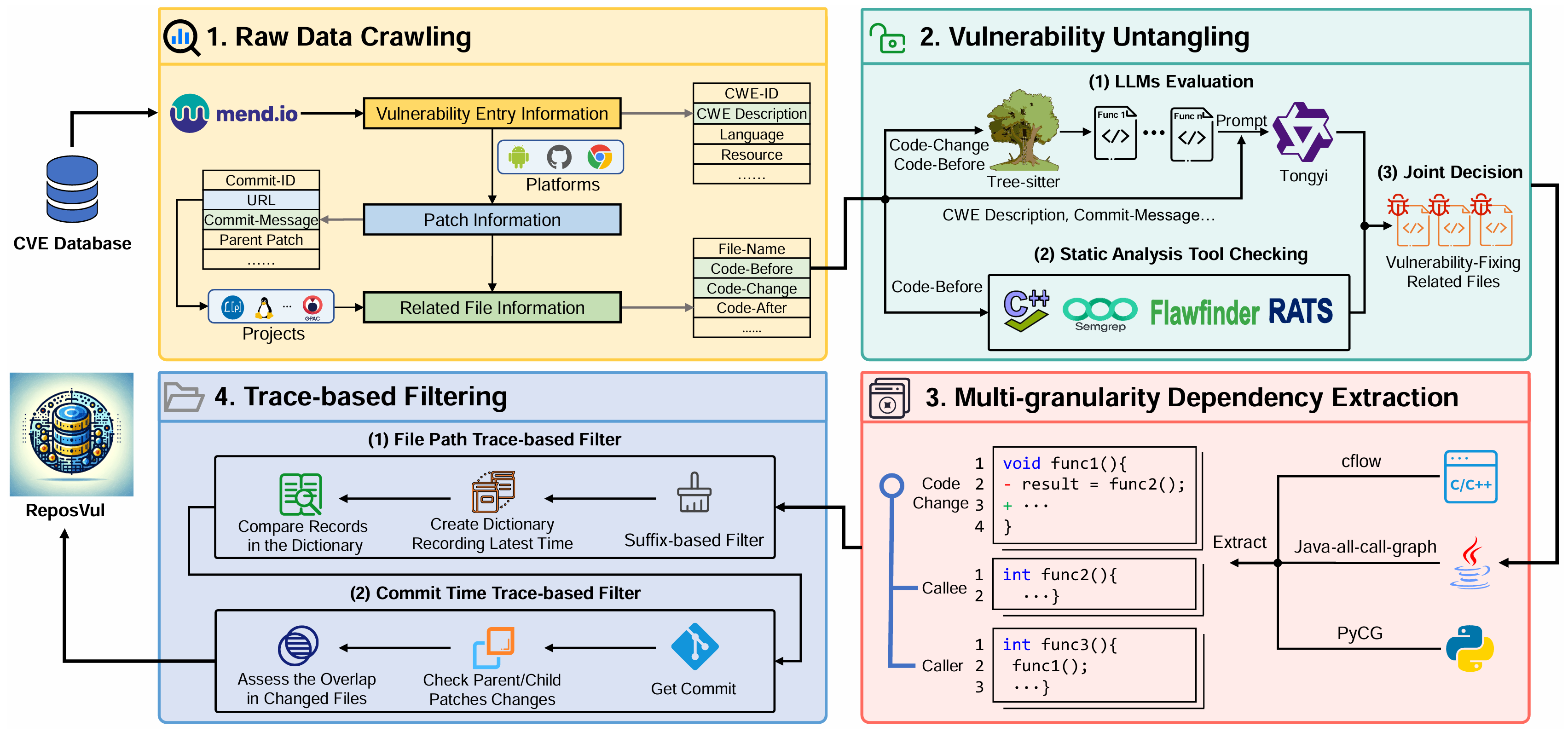
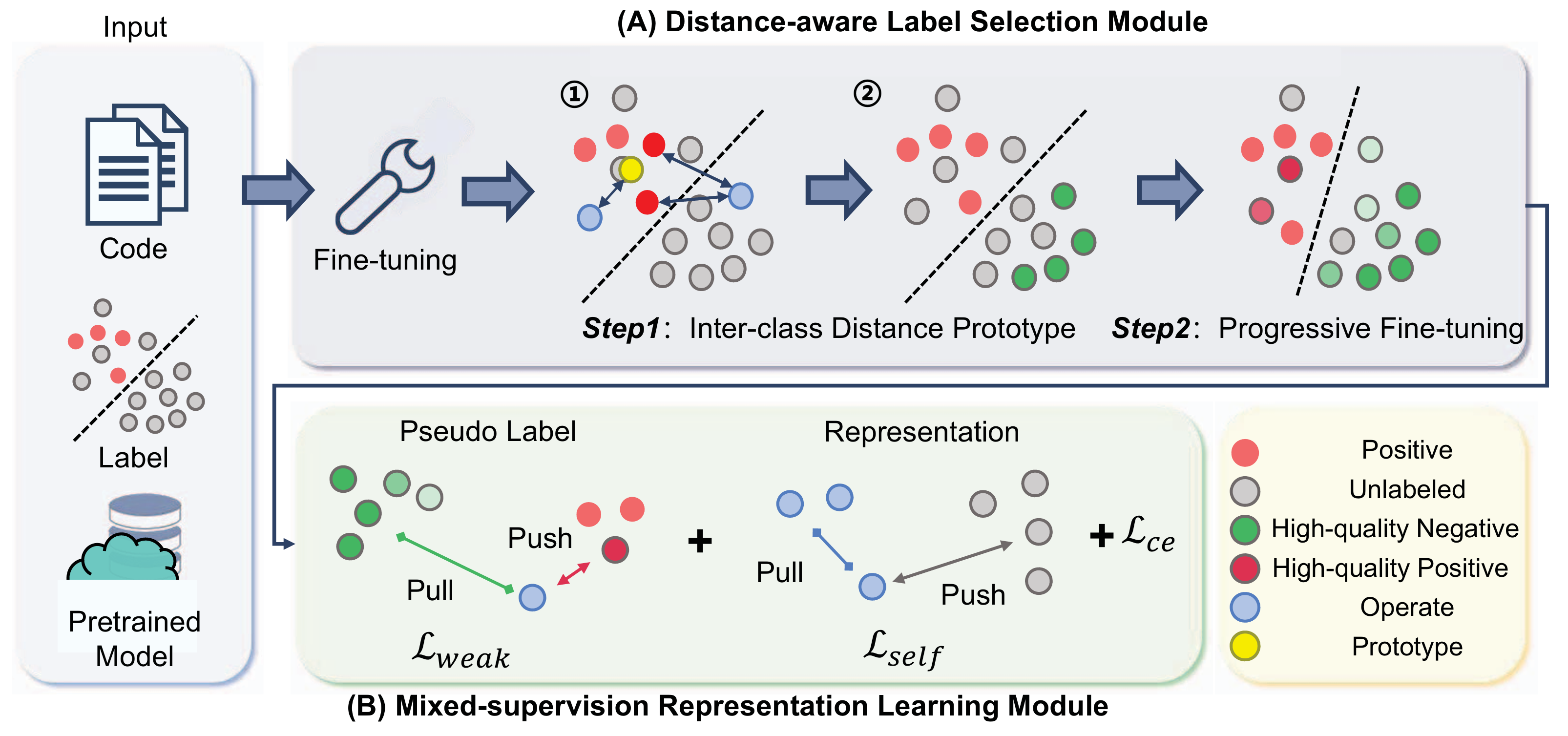
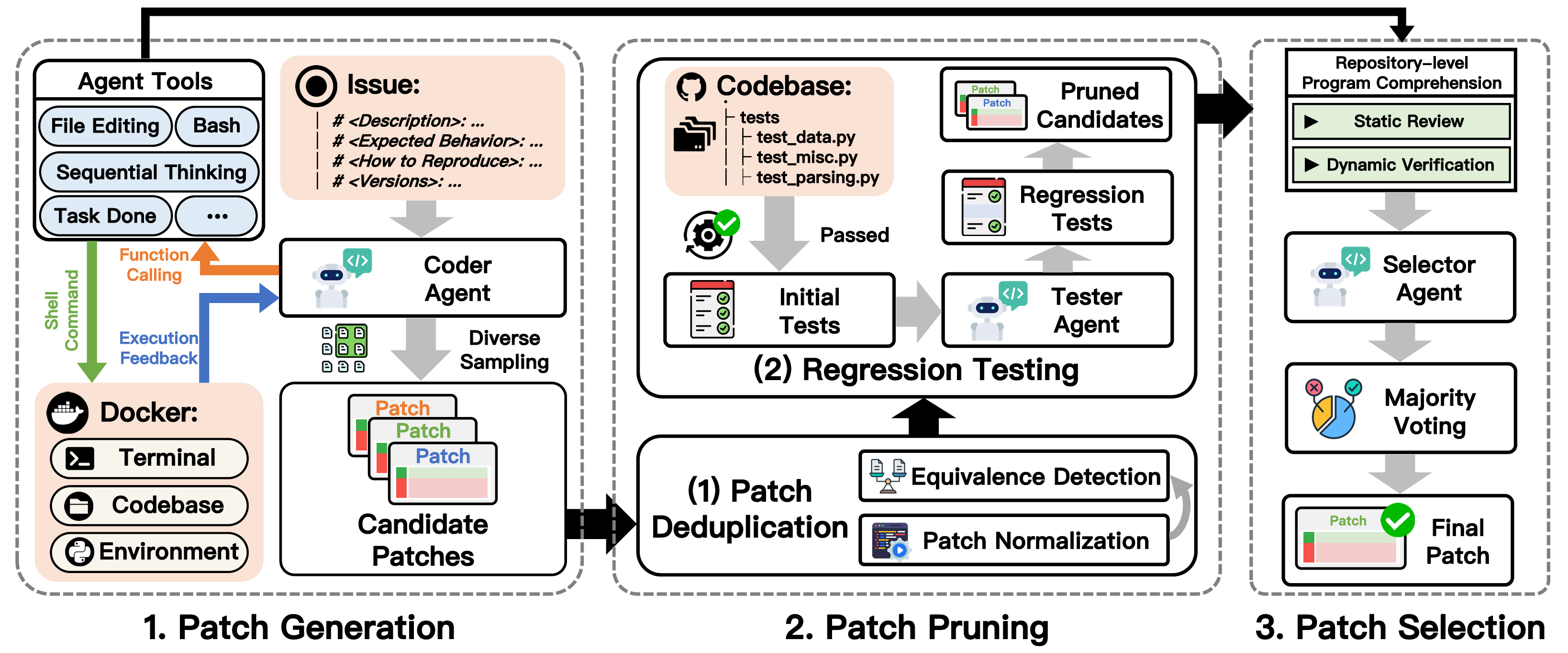
I am a master's student in the School of Computer Science and Technology at Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen. I have the privilege of being advised by Prof. Cuiyun Gao. I received my Bachelor's degree from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen. My research interests primarily focus on Artificial Intelligence for Software Engineering (AI4SE) and Code Intelligence.
I welcome any communication, so feel free to reach out! You can contact me via email at 200111115@stu.hit.edu.cn or on WeChat at gghhzzxhkazz22.